A slewing drive is a gearbox and it can safely hold radial and axial loads, as well as transmit a torque for rotating. The rotation can be in a single axis, or in multiple axes together. Slewing drives consist of gearing, bearings, seals, housing, motor and other auxiliary components.
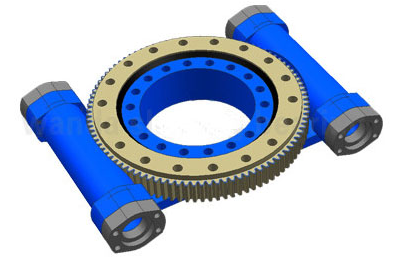
A quality modern slewing drive includes a sound mounting structure, a slew bearing, rotational movement and power controls to facilitate perfect motion. In operation, the drive converts axial movement (force exerted on an axis) into radial/rotary torque, allowing the rotation of greater loads with more accuracy, while also enabling geared torque amplification.
The slewing drive does this by meshing the grooves of a horizontal screw (the worm) with the teeth of a gear placed perpendicular to the screw. The gear rotates as the screw turns, and the screw’s axial movement force is then transmitted to the radial gear as magnified output torque.
The physics of the slew drive makes it a versatile solution for many applications. In operation, the slew drive’s axial movement, or motion around its axis, interacts to create radial torque. The action occurs by meshing the grooves of the horizontal screw with the teeth of a perpendicular gear. While turning, the worm gear’s axial movement transfers magnified torque force to the radial gear. The number of threads on the horizontal screw and the number of gears that interact will determine the speed ratio of the setup.
The slewing drives can be single axis slewing drive or two axis slewing drive